Assessment of Coastal Erosion & Land Loss in Indian Sundarbans - A Case Study Using Remote Sensing & Geographic Information System
Explore the impact of coastal erosion and land loss in the Indian Sundarbans through a compelling case study that employs remote sensing and geographic information system (GIS) techniques. Gain insights into the intricate dynamics of this vulnerable region and its implications for environmental conservation and sustainable development. Discover the potential of innovative technologies in monitoring and understanding coastal changes for effective management strategies.

Introduction
Coastal erosion and land loss pose significant challenges in various parts of the world, and one such region is the Indian Sundarbans. This article aims to provide a comprehensive assessment of coastal erosion and land loss in the Indian Sundarbans, utilizing remote sensing and Geographic Information System (GIS) techniques. By understanding the causes, impacts, and potential mitigation strategies, we can gain valuable insights into the preservation of this ecologically diverse and vulnerable region.
Understanding the Indian Sundarbans
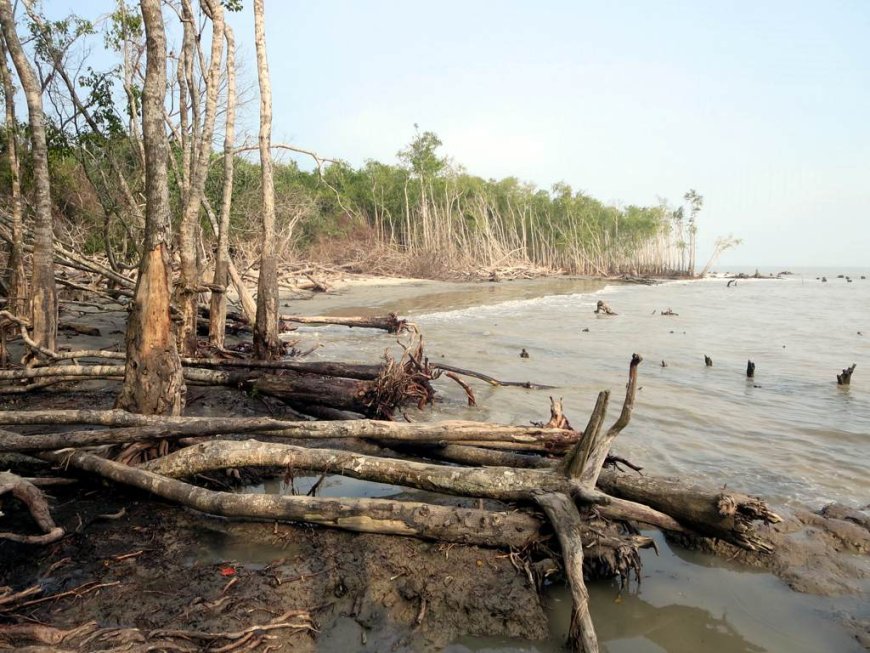
The Indian Sundarbans is a vast mangrove forest situated in the coastal region of the Bay of Bengal, spanning across parts of India and Bangladesh. It is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site and is renowned for its unique biodiversity. The Sundarbans serves as a crucial habitat for numerous species, including the endangered Bengal tiger.
Coastal Erosion: Causes and Impacts
Coastal erosion refers to the gradual wearing away of land along coastlines due to natural and anthropogenic factors. In the case of the Indian Sundarbans, several factors contribute to coastal erosion. These include:
1. Sea Level Rise
One of the primary causes of coastal erosion in the Indian Sundarbans is sea level rise. Due to climate change and global warming, the sea levels have been steadily increasing, resulting in the encroachment of seawater into the land areas. The rise in sea level accelerates the erosion process, leading to the loss of valuable land.
2. River Sediment Discharge
The Sundarbans is situated at the confluence of several major rivers, including the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna. These rivers carry vast amounts of sediment, which helps in replenishing and stabilizing the land in the deltaic region. However, factors such as upstream dams and embankments disrupt the natural sediment flow, depriving the Sundarbans of essential sediment deposits and exacerbating the erosion problem.
3. Cyclones and Storm Surges
The Indian Sundarbans is prone to frequent cyclones and storm surges, which have devastating consequences for the coastal areas. These natural disasters lead to the erosion of land, destruction of vegetation, and increased vulnerability of local communities. The combination of high winds and tidal surges intensifies the erosion process, leaving behind a trail of devastation.
Remote Sensing and GIS in Assessing Coastal Erosion
Remote sensing and Geographic Information System (GIS) technologies play a vital role in studying and monitoring coastal erosion in the Indian Sundarbans. These advanced tools allow scientists and researchers to gather accurate and detailed data, enabling a better understanding of the erosion patterns, trends, and impacts. Some key applications of remote sensing and GIS in assessing coastal erosion include:
1. Change Detection
Remote sensing data, such as satellite imagery, can be compared over time to detect changes in the coastal landforms. By analyzing the differences in land extent and vegetation cover, researchers can identify areas experiencing erosion and quantify the rate of land loss. This information is crucial for formulating effective mitigation strategies.
2. Shoreline Mapping
GIS technology enables the creation of precise shoreline maps, providing valuable information about the shifting coastline. By analyzing historical shoreline data, scientists can identify areas that have experienced the most significant erosion and prioritize them for conservation efforts. This spatial analysis helps in understanding the spatial distribution of erosion and its underlying causes.
3. Vulnerability Assessment
Through the integration of remote sensing and GIS, vulnerability assessments can be conducted to determine the susceptibility of different regions within the Sundarbans to coastal erosion. By considering various factors such as sea level rise, sediment deposition, and vegetation cover, researchers can identify areas at high risk and develop targeted adaptation measures.
Mitigation Strategies for Coastal Erosion
Addressing coastal erosion and land loss in the Indian Sundarbans requires a multi-faceted approach that combines scientific research, policy interventions, and community participation. Some potential mitigation strategies that can be employed include:
1. Nature-Based Solutions
Implementing nature-based solutions, such as mangrove restoration and afforestation, can significantly contribute to reducing coastal erosion. Mangroves act as natural barriers, protecting the land from the impact of waves and tides. By restoring and expanding mangrove forests, the resilience of the Sundarbans ecosystem can be enhanced, mitigating the effects of erosion.
2. Sustainable Land Use Practices
Promoting sustainable land use practices is crucial for mitigating coastal erosion. This involves implementing regulations and guidelines for activities such as aquaculture, agriculture, and tourism to ensure they are conducted in an environmentally responsible manner. By minimizing the negative impacts of human activities, the Sundarbans can be better protected against erosion.
3. Community Engagement and Education
Engaging local communities and raising awareness about the importance of coastal conservation is paramount. By involving communities in decision-making processes and providing them with the necessary knowledge and skills, they can actively participate in the protection and restoration of the Sundarbans. Community-based initiatives, such as eco-tourism and livelihood programs, can contribute to sustainable development while preserving the fragile coastal ecosystem.
Utilizing Remote Sensing for Assessment
Remote sensing plays a pivotal role in assessing coastal erosion and land loss. It involves the acquisition and interpretation of data from aerial or satellite platforms to study changes in land cover, shoreline dynamics, and vegetation patterns over time. In the case of the Indian Sundarbans, remote sensing enables us to monitor the extent of erosion, track sediment deposition, and identify areas at high risk.
Satellite Data Sources
Several free satellite data sources are available for conducting assessments in the Indian Sundarbans. These include:
Landsat: The Landsat program provides valuable multispectral imagery that aids in monitoring land cover changes and analyzing coastal dynamics. The Landsat satellites capture data at regular intervals, allowing for temporal analysis.
Sentinel: The Sentinel series of satellites, launched by the European Space Agency, offer high-resolution imagery and synthetic aperture radar (SAR) data. These sensors provide valuable information on land cover, shoreline changes, and coastal vegetation.
MODIS: The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) sensors onboard NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites provide near real-time data on land cover, sea surface temperature, and vegetation indices. MODIS data is particularly useful for studying large-scale environmental changes.
ASTER: The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) sensor, aboard NASA's Terra satellite, captures high-resolution imagery in multiple spectral bands. This data is useful for detailed land cover classification and landform analysis.
Software Methodology for Analysis
To analyze the satellite data and assess coastal erosion in the Indian Sundarbans, Geographic Information System (GIS) software is instrumental. GIS allows for the integration of spatial data, enabling researchers to analyze, model, and visualize the changes occurring in the coastal zone. Some widely used GIS software for coastal erosion assessment are:
ArcGIS: Developed by Esri, ArcGIS is a comprehensive GIS platform that offers a range of tools for data analysis, geoprocessing, and cartographic visualization. Its advanced functionalities make it suitable for complex coastal erosion studies.
QGIS: An open-source GIS software, QGIS provides a user-friendly interface coupled with powerful geospatial analysis capabilities. It supports various plugins and algorithms for coastal erosion assessment, making it a popular choice among researchers.
ENVI: ENVI is an advanced remote sensing and image analysis software that offers specialized tools for coastal monitoring. It provides a wide range of algorithms for image classification, change detection, and terrain analysis.
By employing these software methodologies and integrating satellite data, researchers can generate accurate maps, quantify erosion rates, and assess the impact of human interventions on the coastal ecosystem.
The Role of Policy and Governance
Effective policy and governance frameworks play a crucial role in addressing coastal erosion and land loss in the Indian Sundarbans. It is essential to establish regulations and guidelines that promote sustainable development while ensuring the protection of coastal ecosystems. Key aspects of policy and governance in this context include:
1. Integrated Coastal Zone Management
Implementing an integrated coastal zone management approach is vital for sustainable development in the Sundarbans. This involves coordinating various sectors, such as fisheries, forestry, tourism, and infrastructure, to ensure that activities are aligned with the conservation of coastal resources. Integrated planning and management strategies can minimize conflicts and promote the long-term resilience of the Sundarbans.
2. Stakeholder Collaboration
Bringing together diverse stakeholders, including government agencies, research institutions, non-governmental organizations, and local communities, is crucial for effective decision-making and implementation. Collaborative platforms and participatory processes can facilitate knowledge exchange, capacity building, and the formulation of holistic solutions to address coastal erosion.
3. Monitoring and Evaluation
Regular monitoring and evaluation are essential to assess the effectiveness of mitigation strategies and make informed decisions. It is necessary to establish monitoring programs that track erosion rates, vegetation health, water quality, and other relevant parameters. By analyzing the data collected, policymakers can adapt and refine their strategies to ensure optimal outcomes.
The Economic Significance of the Sundarbans
Beyond its ecological value, the Sundarbans holds significant economic importance for the surrounding communities and the wider region. The mangrove forest provides valuable resources and services, including:
1. Fisheries
The Sundarbans support a thriving fishing industry, providing livelihoods to numerous communities. The estuarine and coastal waters are rich in fish species, including commercially valuable ones. Sustainable fishing practices, coupled with effective management measures, can ensure the continued productivity of fisheries while safeguarding the ecosystem.
2. Tourism
The unique biodiversity and natural beauty of the Sundarbans attract tourists from around the world. Responsible and sustainable tourism can generate economic benefits for local communities, supporting livelihoods and fostering socio-economic development. It is essential to promote tourism activities that minimize environmental impacts and respect the cultural heritage of the region.
3. Carbon Sequestration and Climate Regulation
The Sundarbans play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. The dense mangrove vegetation acts as a carbon sink, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Protecting and restoring the Sundarbans is, therefore, not only important for local communities but also for global efforts to combat climate change.
The Way Forward
Preserving the Indian Sundarbans requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders involved. Here are some key considerations for the way forward:
1. Continued Research and Innovation
Investing in research and innovation is essential to deepen our understanding of coastal erosion processes, improve monitoring techniques, and develop innovative solutions. By supporting scientific endeavors, policymakers can make informed decisions based on the latest evidence and expertise.
2. International Cooperation
Coastal erosion and land loss are global challenges that require international collaboration. Sharing knowledge, best practices, and financial resources can enhance the effectiveness of conservation efforts in the Sundarbans. Bilateral and multilateral partnerships can facilitate the exchange of experiences and promote joint initiatives.
3. Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Addressing the root causes of coastal erosion necessitates concerted efforts to mitigate climate change. This involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting renewable energy sources, and adapting to the changing climate. By integrating climate change considerations into policies and strategies, the Sundarbans can better withstand the impacts of sea-level rise and extreme weather events.
In conclusion, the assessment of coastal erosion and land loss in the Indian Sundarbans is a complex task that requires a multidisciplinary approach. Through the application of remote sensing, GIS technologies, and robust scientific research, we can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of coastal erosion. By implementing sustainable mitigation strategies, engaging local communities, and fostering international cooperation, we can safeguard the Sundarbans' ecological integrity and ensure its continued contribution to biodiversity conservation, sustainable livelihoods, and climate change mitigation.
The Importance of Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about coastal erosion and land loss is crucial for garnering support and driving positive change in the Indian Sundarbans. Education plays a vital role in empowering individuals and communities to become stewards of their environment. Some key aspects to consider include:
1. Environmental Education Programs
Developing comprehensive environmental education programs can help instill a sense of responsibility and environmental consciousness among the local population. These programs can be designed to educate individuals about the importance of coastal ecosystems, the impacts of erosion, and the role they can play in conservation efforts. By fostering a deeper understanding, we can inspire action and encourage sustainable practices.
2. Community Engagement
Engaging local communities in the decision-making process is essential for long-term success. By involving community members in coastal restoration projects, awareness campaigns, and monitoring initiatives, they can become active participants and advocates for the preservation of the Sundarbans. Building strong partnerships and fostering a sense of ownership can lead to more effective and sustainable conservation outcomes.
3. Collaboration with Schools and Universities
Collaborating with educational institutions, including schools and universities, can help integrate environmental topics into the curriculum. By incorporating lessons on coastal erosion, climate change, and conservation, we can equip the younger generation with the knowledge and skills necessary to become future environmental leaders. Field trips and research opportunities can further enhance their understanding and appreciation of the Sundarbans.
Economic Opportunities and Sustainable Livelihoods
While addressing coastal erosion and land loss is crucial, it is also essential to consider the economic well-being of the local communities dependent on the Sundarbans. Sustainable livelihood options can be explored to provide alternative sources of income while ensuring the protection of the environment. Some potential avenues include:
1. Eco-Tourism
Promoting responsible and sustainable eco-tourism can create economic opportunities for local communities. By offering guided tours, nature walks, and cultural experiences, tourists can appreciate the unique beauty of the Sundarbans while supporting the livelihoods of the residents. It is important to strike a balance between tourism development and environmental conservation, ensuring minimal ecological impact.
2. Community-Based Enterprises
Encouraging the establishment of community-based enterprises can provide income diversification for the local population. This can include activities such as handicraft production, organic farming, and sustainable aquaculture practices. By focusing on environmentally friendly practices, these enterprises can contribute to the preservation of the Sundarbans while generating income for the community.
3. Research and Ecological Monitoring
Investing in research and ecological monitoring initiatives can create employment opportunities for individuals with a passion for environmental conservation. By supporting scientific research projects and employing local researchers and field assistants, we can build local capacity and contribute to the body of knowledge about the Sundarbans. These efforts can also lead to informed decision-making and evidence-based conservation strategies.
The Role of International Support
Given the global significance of the Sundarbans and the challenges it faces, international support is crucial in preserving this unique ecosystem. Cooperation and assistance from the international community can contribute to effective conservation efforts. Some key areas where international support can make a difference include:
1. Funding for Research and Conservation Projects
Financial support from international organizations, governments, and philanthropic foundations can help fund research projects, conservation initiatives, and capacity-building programs. These funds can be utilized to conduct scientific studies, implement restoration projects, and train local communities in sustainable practices. By investing in the Sundarbans, the international community can contribute to its long-term preservation.
2. Knowledge Exchange and Technical Expertise
International collaboration facilitates the exchange of knowledge, best practices, and technical expertise. Researchers and experts from around the world can provide valuable insights and guidance on coastal erosion management, sustainable development, and climate change adaptation. By leveraging international expertise, local stakeholders can benefit from innovative approaches and strategies.
3. Advocacy and Policy Support
International organizations and diplomatic channels play a crucial role in advocating for the protection of the Sundarbans at a global level. By raising awareness about its ecological significance and the challenges it faces, they can mobilize support and influence policy decisions. International agreements and frameworks can also provide a platform for addressing cross-border issues and promoting regional cooperation.
The Way Forward: A Shared Responsibility
Preserving the Indian Sundarbans requires a shared responsibility and a collective effort from all stakeholders. Here are some key actions that can guide the way forward:
1. Integrated Management and Planning
Integrating management efforts across sectors and jurisdictions is essential for effective conservation. A comprehensive and integrated approach that considers ecological, social, and economic aspects can ensure the sustainable development of the Sundarbans while protecting its fragile ecosystem. This requires collaboration and coordination among government agencies, research institutions, local communities, and other stakeholders.
2. Climate Change Adaptation
Given the impacts of climate change, it is crucial to prioritize climate change adaptation strategies in the Sundarbans. This includes enhancing resilience to sea-level rise, strengthening infrastructure, and promoting nature-based solutions. By incorporating climate considerations into policies and planning, the Sundarbans can better withstand the challenges posed by a changing climate.
3. Empowering Local Communities
Empowering local communities and involving them in decision-making processes is essential. Recognizing their traditional knowledge, promoting sustainable livelihood options, and providing access to education and resources can help create a sense of ownership and foster their active participation in conservation efforts. Community-based management approaches can ensure the long-term success and sustainability of conservation initiatives.
Conclusion
In conclusion, addressing coastal erosion and land loss in the Indian Sundarbans requires a holistic approach that encompasses scientific research, community engagement, education, and sustainable economic development. By integrating these aspects, we can create a synergistic framework that ensures the long-term preservation of this invaluable ecosystem.
Through public awareness campaigns, environmental education programs, and collaboration with local communities, we can foster a sense of responsibility and stewardship towards the Sundarbans. Simultaneously, by exploring sustainable livelihood options and economic opportunities, we can strike a balance between conservation and the well-being of local populations.
It is imperative that all stakeholders, including government bodies, researchers, NGOs, and local communities, work together to protect and restore the Indian Sundarbans. By doing so, we can secure a sustainable future for this ecologically significant region and ensure that it continues to thrive for generations to come.
Data Sources:
Satellite Imagery: Obtain satellite imagery from freely available sources such as:
Landsat: USGS EarthExplorer (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/)
Sentinel-2: Copernicus Open Access Hub (https://scihub.copernicus.eu/)
Digital Elevation Models (DEM):
SRTM (Shuttle Radar Topography Mission) data: USGS EarthExplorer (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/)
ASTER GDEM (Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer Global Digital Elevation Model): NASA's Earthdata Search (https://search.earthdata.nasa.gov/)
Other Data:
Coastline and land-use data: National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC) - India (https://bhuvan.nrsc.gov.in/)
Software:
Geographic Information System (GIS) Software:
QGIS (Quantum GIS): Open-source GIS software (https://www.qgis.org/)
ArcGIS Online: Web-based GIS platform with free access to some features (https://www.arcgis.com/)
Google Earth Engine: Cloud-based platform for geospatial analysis (https://earthengine.google.com/)
Remote Sensing Analysis:
ENVI: Commercial software for remote sensing image analysis (https://www.l3harris.com/envi)
SNAP (Sentinel Application Platform): Free and open-source software for processing Sentinel data (https://step.esa.int/main/toolboxes/snap/)
What's Your Reaction?