Unlocking the Potential of Geoinformatics: How Technology is Revolutionizing Environmental Management
Discover how geoinformatics, the science of analyzing geospatial data, is transforming environmental management. Learn how it helps to map, monitor and manage environmental issues, supports decision-making, promotes public engagement, and addresses environmental injustice. Despite the challenges, the benefits of geoinformatics are vast and essential to understanding and managing environmental issues. Find out how this powerful tool is revolutionizing the way we approach environmental conservation and sustainability.

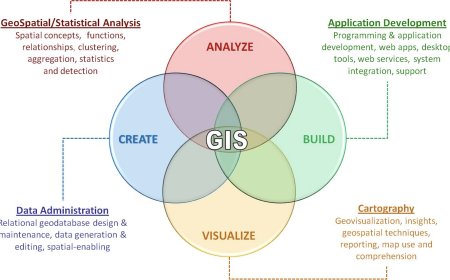
Geoinformatics is a rapidly growing field that plays a critical role in environmental management. This field involves collecting, analyzing, and managing geospatial data using various technologies and tools. Geospatial data is any data that contains a geographic component, such as location, elevation, or land use. By analyzing this data, geoinformatics provides valuable insights into environmental patterns, trends, and relationships that help to better understand and manage environmental issues.
How Technology is Revolutionizing Environmental Management
Geoinformatics can be used in a variety of ways to support environmental management efforts. Here are some examples:
1.Mapping and monitoring environmental features: Geoinformatics can be used to create maps of environmental features such as wetlands, forests, or wildlife habitats. These maps can then be used to monitor changes in these features over time, allowing for better management and conservation efforts.
2.Modeling environmental processes: Geoinformatics can be used to model environmental processes such as water flow, nutrient cycling, or land use changes. These models can help environmental managers understand how changes to the environment will impact these processes and develop strategies to mitigate negative effects.
3.Identifying areas of environmental risk: Geoinformatics can be used to identify areas that are at risk of environmental damage or degradation, such as areas with high levels of pollution or erosion. This information can then be used to prioritize environmental management efforts and target resources where they are most needed.
4.Monitoring environmental compliance: Geoinformatics can be used to monitor compliance with environmental regulations, such as monitoring emissions from factories or tracking the movement of hazardous waste. This can help ensure that environmental regulations are being followed and identify areas where improvements are needed.
5.Supporting emergency response efforts: Geoinformatics can be used to support emergency response efforts in the event of an environmental disaster, such as a natural disaster or oil spill. Geospatial data can be used to quickly identify impacted areas and direct response efforts to where they are needed most.
Furthermore, geoinformatics is also useful in identifying areas of environmental injustice, where vulnerable populations may be disproportionately affected by environmental hazards. By analyzing geospatial data on demographics, environmental hazards, and social vulnerability, geoinformatics can help identify areas where environmental justice is lacking and guide efforts to address these issues.
Geoinformatics also supports decision-making in environmental management. The data provided by geoinformatics can help stakeholders make informed decisions on issues related to environmental conservation and sustainability. For instance, policymakers can use geoinformatics data to make decisions on land use, development, and environmental regulations. Additionally, businesses can use geoinformatics to make decisions related to sustainability initiatives, such as reducing their carbon footprint or adopting environmentally friendly practices.
Finally, geoinformatics can help to promote public engagement and education on environmental issues. By presenting geospatial data in an accessible and understandable manner, stakeholders can better understand the impact of their actions on the environment. This can encourage them to adopt more sustainable practices and support environmental conservation efforts.
Mapping and Monitoring Environmental Features
One of the primary applications of geoinformatics in environmental management is mapping and monitoring environmental features. For instance, geoinformatics can be used to create maps of wetlands, forests, wildlife habitats, and other environmental features. These maps are then used to monitor changes in these features over time, which helps to manage and conserve them better. By monitoring changes, environmental managers can create better strategies to address any issues affecting the environment.
Modeling Environmental Processes
Geoinformatics can also be used to model environmental processes such as water flow, nutrient cycling, or land use changes. These models can help environmental managers understand how changes to the environment impact these processes and develop strategies to mitigate negative effects. For instance, geoinformatics can help predict the impact of development on an environment and advise on ways to mitigate its effects.
Identifying Areas of Environmental Risk
Geoinformatics can also be used to identify areas of environmental risk. It can detect areas that are at risk of environmental damage or degradation such as pollution, deforestation, or soil erosion. This information is used to prioritize environmental management efforts and allocate resources where they are most needed. For instance, geoinformatics can help identify areas that need immediate attention and remedial action to mitigate risks to the environment.
Monitoring Environmental Compliance
Another important application of geoinformatics in environmental management is monitoring environmental compliance. Geoinformatics can be used to monitor compliance with environmental regulations, such as monitoring emissions from factories or tracking the movement of hazardous waste. This helps to ensure that environmental regulations are being followed and identify areas where improvements are needed. For instance, geoinformatics can help identify companies or industries that fail to comply with environmental regulations and recommend measures to curb such practices.
Supporting Emergency Response Efforts
Geoinformatics is also useful in supporting emergency response efforts in the event of an environmental disaster. Geospatial data can be used to quickly identify impacted areas and direct response efforts to where they are needed most. For instance, geoinformatics can help to assess the extent of an oil spill, identify affected areas and wildlife habitats and guide the response team on ways to mitigate the impact.
Challenges
However, there are also some challenges associated with the use of geoinformatics in environmental management. One of the main challenges is the quality and availability of data. Geospatial data can be difficult to collect and may contain errors or inaccuracies. Additionally, some data may not be available or accessible due to issues of data ownership or privacy concerns.
Another challenge is the need for specialized skills and training in geoinformatics. The field requires expertise in data collection, management, analysis, and visualization, as well as knowledge of specific tools and software. As such, there is a need for environmental managers and other stakeholders to have access to training and resources to develop these skills.
Furthermore, there are also ethical concerns related to the use of geoinformatics in environmental management. For instance, there may be issues related to the privacy of individuals or communities in relation to the collection and use of geospatial data. Additionally, there may be issues related to the potential misuse of geospatial data, such as using it to advance economic or political interests at the expense of the environment.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of geoinformatics in environmental management far outweigh the risks. Geoinformatics provides a powerful tool for understanding and managing environmental issues, promoting sustainability, and advancing environmental justice. By leveraging geospatial data and technology, stakeholders can make informed decisions and develop more effective strategies for conserving and protecting the environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, geoinformatics is an essential tool for environmental management. By analyzing geospatial data, geoinformatics provides valuable insights into environmental patterns, trends, and relationships. Its applications range from mapping and monitoring environmental features to supporting emergency response efforts and promoting public engagement and education on environmental issues. With the increasing availability of geospatial data and advances in technology, geoinformatics is becoming an indispensable tool for environmental management. It helps to improve our understanding of the environment and develop more effective strategies for conservation and sustainability.
What's Your Reaction?